Traumatic Injuries
Dental injuries and emergencies are often distressing for both children and parents; at the same time, they are quite common too. They often occur due to damage, injury, or accident. Traumatic injuries can cause damage to tooth enamel, existing restorations, and other teeth structures.
There are two peak risk periods when dental traumas usually happen - the first being toddlerhood (18-40 months), and the second being the preadolescent/adolescent period when sporting injuries become common.
Some of the most common traumatic dental injuries that can happen are:
Dental avulsion (knocked-out tooth)
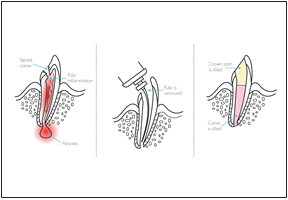
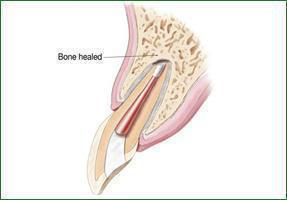
An avulsed tooth is when a tooth has been knocked-out of the socket. When a dental avulsion happens, it is important to seek immediate treatment. Store the knocked-out teeth in a compatible solution such as cold milk or saline solutions before taking it to the dentist. However, in most cases, the pediatric dentist does not attempt to reimplant a knocked-out primary tooth as the process may damage the tooth bud and the emerging permanent teeth too. If it is a permanent tooth, the treatment would generally start with a root canal to restore the avulsed tooth into its socket.
Dental intrusion (tooth pushed into jawbone)
Dental trauma may sometimes push a tooth (or several teeth) upwards into the jawbone. Often, the trauma force is significant enough to injure the tooth's ligament and fracture its socket. If the primary or permanent teeth' dental intrusion is suspected, contact the pediatric dentist immediately. The dentist will either wait for the tooth to descend on its own or conduct root canal therapy, depending on the intrusion's nature and depth.
Dislodged Teeth
Dental trauma can lead to dislodged teeth where the teeth are pushed either sideways or out of the socket, displacing it. It is important to take your child to the dentist if displacement is suspected to save the teeth and prevent infection. An endodontist can reposition the dislodged teeth and eventually stabilize the affected tooth. Dislodged teeth are generally be treated with a root canal and medication.
Crown fracture
In most dental injuries, the crown, which is the largest and most visible part of the tooth, sustains trauma. The crown fracture can range from minor enamel cracks, which is not an emergency, to pulp exposure that requires immediate treatment. The pediatric dentist assesses the severity of the fracture using dental X-rays and plan the treatment accordingly.
Root fracture
A root fracture is caused by direct trauma and is not noticeable to the naked eye. If you ever suffer a dental trauma and suspect a root fracture, seek medical attention immediately. The dentist will take x-rays, and depending on the exact positioning of the fracture; he decides the treatment plan.
Dental concussion
A dental concussion happens when the tooth has not been dislodged from its socket but has received a bang. This usually occurs in toddlers and can cause the tooth to discolor permanently or temporarily. Unless the tooth turns black or dark, that indicates that the tooth is dying and may require root canal therapy, dental concussion does not need emergency treatment.
Injured cheek, lip, or tongue
If the trauma causes injury to the child's cheek, lip, or tongue and is bleeding heavily, apply firm direct pressure to the area using a clean cloth or gauze. Seek medical help immediately if the bleeding becomes uncontrollable.
Fractured jaw
If you suspect that the child's jaw is broken or fractured, proceed immediately to the Emergency Room. Gently tie a scarf lengthways around the head and jaw to prevent the child from moving the jaw.
If you have questions about dental emergencies or have one, call us to schedule an appointment or visit us immediately.